Gut-brain connection
Gut-brain connection is a modern term for connection betwequest salomon manico basso 5 corde amazon selected frakke brun κρεβατια μονα με αποθηκευτικο χωρο και στρωμα vans sandals australia marc jacobs handtassen outlet yeezy shoes for sale scaffalatura cantilever Italy adidas compensée balenciaga sinners hoodie batterie flachpol adapter birkenstock gizeh blau gold batterie flachpol adapter hp 5230 patrone Switzerland adidas nmd girls functions are similar to a second brain?
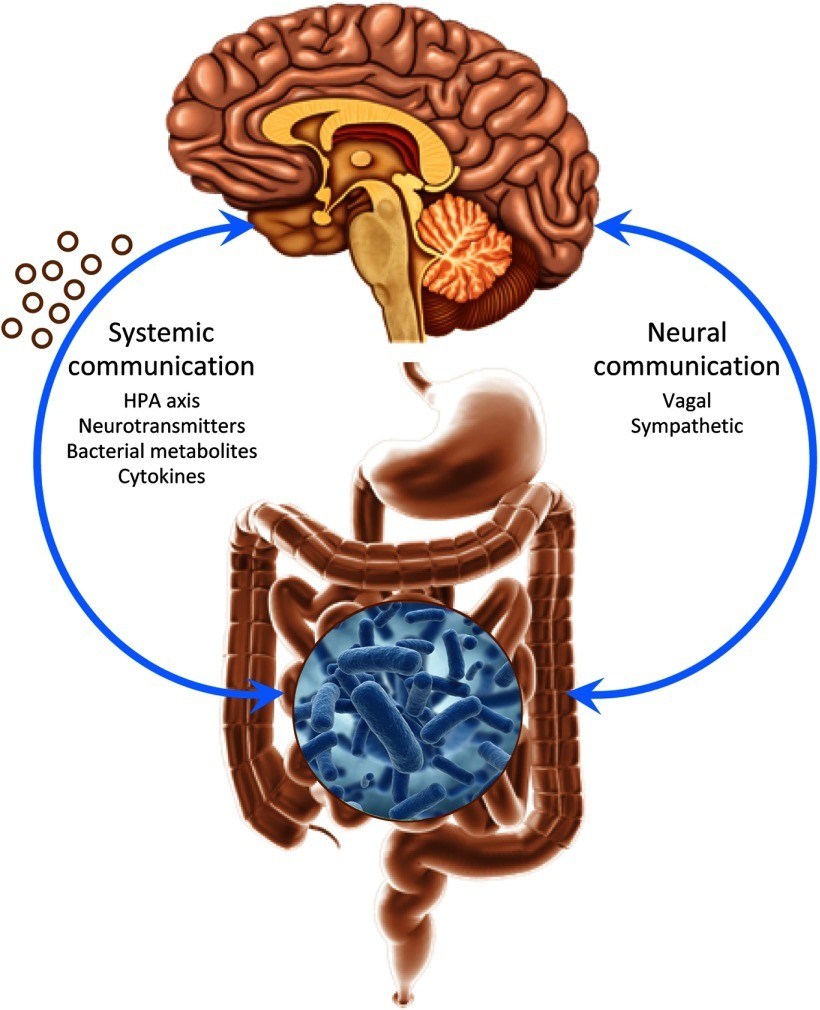 The central nervous system and the autonomic nervous system advance from identical tissues during fetal progress. One of them later in the development process grows the brain, while the other part cultivates the autonomic nervous system.
The central nervous system and the autonomic nervous system advance from identical tissues during fetal progress. One of them later in the development process grows the brain, while the other part cultivates the autonomic nervous system.
These two nervous systems are linked via the Vagal nerve which lets the gut to function as a great, semi-autonomic intelligence with its own intricate endocrine motioning structure. Laboratory and Clinical researches have shown that in this way, the autonomic nervous system can directly influence the brain.
Scientists researchers confirm that both positive and unhealthy microbiome in the abdominal tract can initiate neural corridors and brain signaling
The gastrointestinal bacteria g. may be affected by our environmental and psychological conditions; and as the result, the abdominal bacteria can initiate chemical markers and neurotransmitters, which upset memory, sentimental reactions, and conduct in different lobes of the brain.
Researchers recently discovered that:
- Campylobacter Jejuni contaminations can intensify anxiety
- Abdominal bacteria may increase or decrease nutrients cravings
- Autistic youngsters have not as much of negative gut microbiomes than healthy kids
- People who are suffering from anorexia nervosa have considerably lower than normal level of the stomach microbiomes
- Some antibiotics may prompt psychotic conditions
In conclusion, some central neurological conditions may perhaps start in the stomach and thus harmonizing the digestive system’s bacteria could be the strategic basis to healing approach for these disorders.
One of the most effective approaches for reconditioning of the gastrointestinal flora is by augmenting it with the spore-based supplements: Megaspore Biotic, Florassist® GI, Probiotic All-Flora™, Advance Restorative Probiotic, Dynamic biotic, etc.
It is scientifically proven fact, that the probiotics increase bacterial variety in the GI system by 40-45%.
The Gut-Brain Connection mechanism and importance of Diet
Many patients report that they have strange feelings in their stomach – feeling of butterflies, rocks, worms, rats, etc.
Those sensations originating from the GI system happen because the central nervous system and gut are allied.
Even more, the latest studies demonstrate the effect of brain condition on abdominal health and opposite, the effect of abdominal condition on brain health.
The linkage between the abdomen and the central nervous system known as the gut-brain connection.
The post below discovers the mechanism of the gut-brain connection and nutrition favorable to its wellbeing.
Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection is a term mixture that defines the linked system, which is joining the GI system to the head and mind.
These two configurations are connected extensively, materially, immensely, and biochemically in numerous various manners.
The Vagus Nerve and its connection to the Nervous System
Neurons are the cells invented in a brain and different areas of the central nervous system that keep under control the working and conduct of the body in general. There are nearly 100 billion neurons that combined into the human’s brain. At the same time, a gut in average consists of 500 million neurons and these 500 million nerve cells are linked to a brain through nerves in nervous systems (central, peripheral and autonomic).
The Vagus nerve is one of the largest nerves that connects the abdominal system and central nervous system sending electric and biochemical signals in both directions.
In the most recent experiments on animals, scientists discovered that stress obstructs the signals sent from end to end of the Vagus nerve and thus leads to gastrointestinal diseases.
In the same way, researches performed in humans’ population found that patients who suffer from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and/or Crohn’s disease have a decline of Vagal activities.
An attention-grabbing study in healthy rats brings to scientists’ attention that adding a probiotic to their food decreased the level of stress hormones (Adrenaline, Cortisol, Norepinephrine) in their bloodstream. When the Vagus nerve blocked (cut, removed, or chemically blocked), the probiotic has no such effect.
This study proves that the Vagus nerve is essential in the gut-brain connection and stress management.
Neurotransmitters and gut-brain connection
The gastrointestinal system and central nervous system are also related with the help of chemicals known as neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters manufactured by the nervous system regulate moods, spirits, and reactions.
Well-known neurotransmitter serotonin, for example, leads to an emotional state of happiness and also controls the biological clock.
Remarkably, numerous of these neurotransmitters are manufactured by the cells of the gastrointestinal system and the trillions of beneficial for organism bacteria living there. Also, a huge amount of serotonin is produced in these microbiomes.
The intestinal bacteria also manufacturing the neurotransmitter known as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA helps to keep feelings of phobia and anxiety under control.
Laboratory studies on rats found that some probiotics may increase the amount of GABA manufactured by a body and thus reduce the level of anxiety and depression.
Microbiomes Manufacture Chemicals, which Have an emotional impact.
The trillions of bacteria that reside in a gut produce other elements that control brain functions.
Some of these elements fall under the category of so-called short-chain fatty acids (SCFA). Butyrate, Acetate, and Propionate represent this category.
Gut microbiomes produce SCFA as a result of fiber consumption. SCFA elements known as appetite depressing, which means to decrease the appetite and be able to stay on low calories diet patients need to consume more food that contains fiber (vegetables).
A few studies brought into being that propionate consumption decreases food demand and the functions in the central nervous system that is rewarding from high-energy products.
Butyrate, another SCFA element and the bacteria that manufacture it are also essential for establishing the blockade between the central nervous system and the body fluid aka blood-brain barrier.
Gut bacteria as well as metabolizing bile acids and amino acids to create other elements that affect the central nervous system.
Bile acids produced by a liver and they help to absorb dietary fats. Nevertheless, they affect the functions of a brain causing some aggressiveness and nervousness.
A few studies in rats discovered that stress and social disorders diminish the manufacture of bile acids by gut microbes and even change some genes that are controlling their fabrication.
Intestinal Bacteria affect the immune system
The immune system is another part of the body that is connected to a gastrointestinal system thru the gut-brain connection</strong犀利士
>.
Gut microbiomes and GI itself play a significant role in the development of the immune system, its activity, and effectiveness. Gastrointestinal system in general and gut microbes, in particular, control the level of inflammation by monitoring everything that is delivered into the body from outside and what is defecated.
If the immune system is inactive for a long time, an inflammation of different organs may happen, and if the organ affected by inflammation is brain it may cause initiation of a number of brain disorders:
- meningitis
- migraines
- anxiety
- depression
- Alzheimer’s disease.
For example, Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a toxin manufactured by some bacteria. It can cause inflammation if leaky gut barrier allows too much of LPS in the bloodstream.
Infection, irritation, tenderness, and raised LPS in a blood flow linked with numerous brain ailments such as deep depression, dementia, derangement, and schizophrenia.
SUMMARY Gut inside a body linked to a brain physically over zillions of nerves, especially the Vagus and Sympathetic nerves. The gut and the bacteria that reside in the gut correspondingly control inflammation and create a variety of dissimilar complexes that may distress brain condition.
Probiotics, Prebiotics, and the Gut-brain connection
The Gut’s microorganisms control the brain well-being, therefore altering your gut microbes would recover your brain vigor.
Probiotics are live microorganisms that benefit general hea犀利士
lth if consumed. Nevertheless, probiotics are different and the use of them should be linked to the particular target that needs to be achieved.
Probiotics that have an emotional impact are usually called “psychobiotics”.
In clinical studies, some psychobiotics decreased the severity of the symptoms of constant worry, nervousness, apprehension, and hopelessness
A few different clinical studies of people with irritable bowel syndrome and mild-to-moderate anxiety or depression proved that consuming for 4-6 weeks a probiotic Bifidobacterium Longum NCC3001 considerably improves patients’ condition.
Prebiotics that are usually fiber containing ingredients work as a food for the bio flora and thus as well improve brain fitness.
A prebiotic Galactooligosaccharides expressively decreased the amount of hormone produced by the adrenal cortex and known as cortisol or hormone of stress.
SUMMARY: Psychobiotics and prebiotics Probiotics may diminish the level of nervousness, constant worry, and depression.
Which Foods are Beneficial for the Gut-Brain Connection?
Several categories of nutrients are explicitly advantageous for the gut-brain affiliation.
- Omega-3 fats: These ingredients discovered in some ocean fishes as well as in a human’s brain. Researches prove that omega-3s upsurge the concentration of the gut microorganisms and thus reducing the risk of brain illnesses.
- Fermented foods: Nutrients manufactured by bacterial fermentation of milk including kefir and yogurt, as well as Tempeh, cheeses, Kombucha, sauerkraut, Kimchi, and Miso hold healthy bacteria such as lactobacilli. These foods can improve brain activity.
- High-fiber foods: Whole grains, fruits and vegetables as well nuts and seeds contain prebiotic fibers that are good for your gut bacteria. Prebiotics help to reduce the level of cortisol (stress hormone) in humans’ body.
- Polyphenol-rich foods: tea (especially green and white), olive oil, Cocoa and coffee all hold an essential concentration of polyphenols, which are natural chemicals manufactured by herbs that are consumed by your gut microorganisms. Polyphenols upsurge healthy gut microbiomes and may progress intellectual development.
- Tryptophan-rich foods: The amino acid Tryptophan, which is transformed into the serotonin (neurotransmitter aka happy chemical or hormone of happiness). Nutriments that are rich in tryptophan are white meat of turkey, organic eggs and different varieties of cheeses.
SUMMARY: Many nutrients: fish oil, fermented and rich in vitamins kinds of pasta as well as rich in fiber products may raise the level of good microorganisms in your gut and recover well-being of a brain.
The Bottom Line of the gut-brain connection
The gut-brain connection speaks of to the corporeal and biochemical influences between intestine, colon, and mind.
Billions of nerves and neurons route between a GI and central nervous system. Neurotransmitters and other self-made by a body substance manufactured in a gut also have an emotional impact on a brain.
By modifying the varieties of microorganisms in a gut, we can improve brain well-being.
Fermented nutrients, Omega-3 acids, life probiotics, and other polyphenol-rich ingredients may advance your wellbeing of an intestine and colon, which and thus improves the gut-brain connection.
If you suffer from any kind of emotional conditions (insomnia, forgetfulness, anxiety, depression, panic attacks, etc.) you may have a problem in a gut-brain connection and nourishing of the healthy gut microbiomes will resolve it.
At the Philadelphia Holistic Clinic, Dr. Tsan and associates will examine you and find out the cause of your emotional instability and pinpoint the treatment to the initial core of the disease.
To schedule your appointment for Initial Alternative Evaluation with Dr. Tsan contact our clinic by calling (267) 403-3085 or use our online system.